Trityl Cation on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
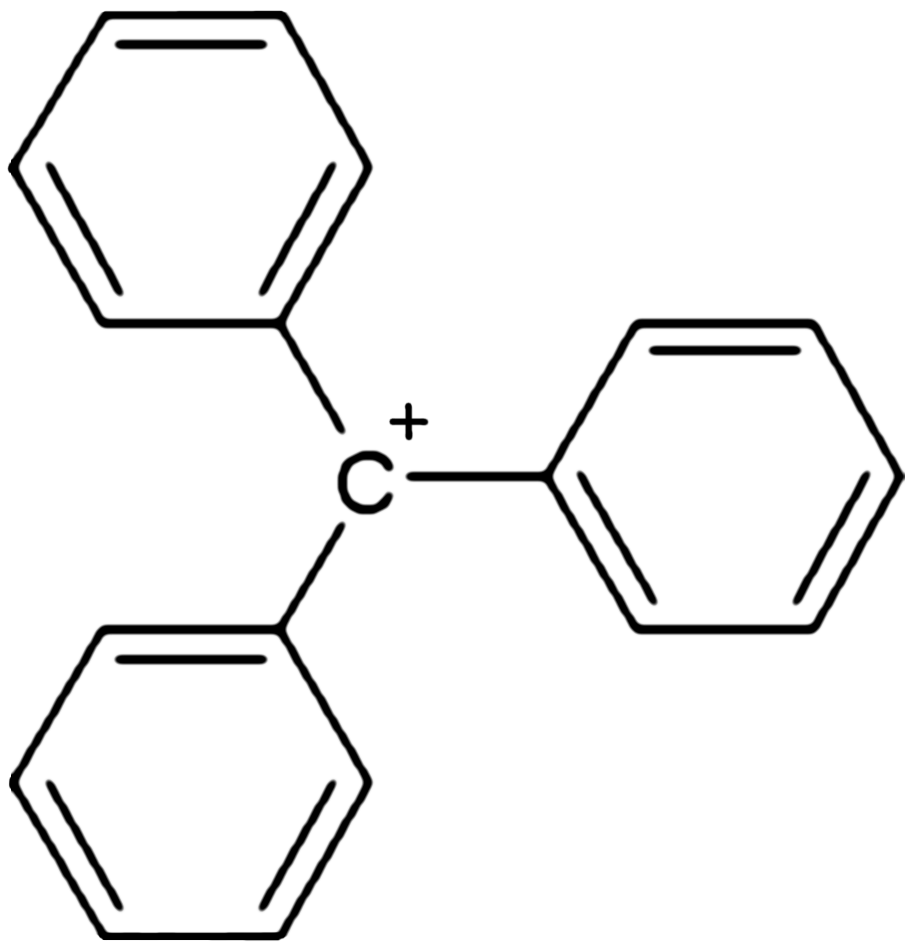
 In chemistry, triphenylcarbenium, triphenylmethyl cation, tritylium , or trityl cation is an
In chemistry, triphenylcarbenium, triphenylmethyl cation, tritylium , or trityl cation is an
Image:Methyl Violet 10B.png,
N. C. Deno, J. J. Jaruzelski, and Alan Schriesheim (1955) "Carbonium ions. I. An acidity function (''C''0) derived from arylcarbonium ion equilibria." ''Journal of the American Chemical Society'', voume 77, issue 11, pages 3044–3051.
Michael E. Jung, Roman Lagoutte, and Ullrich Jahn (2011): "Triphenylcarbenium Tetrafluoroborate". In ''Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis''.
E. Molins, M. Mas, W. Maniukiewicz, M. Ballester and J. Castañer (1996): "Perchlorotriphenylcarbenium Hexachloroantimonate(V)". ''Acta Crystallographica Section C (Structural Chemistry)'', volume C52, pages 2412-2414. {{doi, 10.1107/S0108270196007287
U. S. National Institutes of Health (2019)
PubChem ID 2723954 - Triphenylcarbenium hexafluorophosphate
. Entry in NCBI's PubChem database, accessed on 2019-07-25.
Carbocations

 In chemistry, triphenylcarbenium, triphenylmethyl cation, tritylium , or trityl cation is an
In chemistry, triphenylcarbenium, triphenylmethyl cation, tritylium , or trityl cation is an ion
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge.
The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by conve ...
with formula or , consisting of a carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element with the symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalent—its atom making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds. It belongs to group 14 of the periodic table. Carbon mak ...
atom with a positive charge
Electric charge is the physical property of matter that causes charged matter to experience a force when placed in an electromagnetic field. Electric charge can be ''positive'' or ''negative'' (commonly carried by protons and electrons respe ...
connected to three phenyl
In organic chemistry, the phenyl group, or phenyl ring, is a cyclic group of atoms with the formula C6 H5, and is often represented by the symbol Ph. Phenyl group is closely related to benzene and can be viewed as a benzene ring, minus a hydrogen ...
groups. It is a charged version of the triphenylmethyl radical
The triphenylmethyl radical (often shorted to trityl radical) is an organic compound with the formula (C6H5)3C. It is a persistent radical. It was the first radical ever to be described in organic chemistry. Because of its accessibility, the trit ...
•. The name is often abbreviated to triphenylmethyl or trityl in salts, although these names also denote the chemical group in compounds like triphenylmethyl chloride
Triphenylmethyl chloride or trityl chloride (TrCl) is a white solid with the chemical formula C19H15Cl. It is an alkyl halide, sometimes used to introduce the trityl protecting group.
Preparation
Triphenylmethyl chloride is commercially available. ...
that do not contain the cation.
Triphenylcarbenium is a relatively stable carbenium ion, because the positive charge is partially distributed among 10 of the carbon atoms (the 3 carbon atoms in the ''ortho'' and ''para'' positions of each of the three phenyl groups, plus the central carbon atom).
Derivatives
The cation exists in important chemical reagents andcatalyst
Catalysis () is the process of increasing the rate of a chemical reaction by adding a substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed in the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recyc ...
s such as triphenylmethyl hexafluorophosphate . Related salts are known with diverse anions including (), hexachloroantimonate (), and perchlorate
A perchlorate is a chemical compound containing the perchlorate ion, . The majority of perchlorates are commercially produced salts. They are mainly used as oxidizers for pyrotechnic devices and to control static electricity in food packaging. Per ...
(). This and other similar cations can be obtained as intensely colored solutions by dissolving aryl
In organic chemistry, an aryl is any functional group or substituent derived from an aromaticity, aromatic ring, usually an aromatic hydrocarbon, such as phenyl and naphthyl. "Aryl" is used for the sake of abbreviation or generalization, and "Ar ...
-substituted methanols in concentrated sulfuric acid. Derivatives of this cation include, for example, perchlorotriphenylcarbenium .
Triarylmethane dyes
Triarylmethane dye
Triarylmethane dyes are synthetic organic compounds containing triphenylmethane backbones. As dyes, these compounds are intensely colored. They are produced industrially as dyes.
Families
Triarylmethane dyes can be grouped into families accordin ...
s are derivatives are stabilized version of the trityl cation. They are water-soluble and are often obtained as the chloride salts. These dyes have strong electron donor groups, often amines, at the ''p''-positions of two or three of the aryl groups.Thomas Gessner and Udo Mayer "Triarylmethane and Diarylmethane Dyes" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry
''Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry'' is a major reference work related to industrial chemistry by Chemist Fritz Ullmann, first published in 1914, and exclusively in German as "Enzyklopädie der Technischen Chemie" until 1984.
Hist ...
2002, Wiley-VCH
Wiley-VCH is a German publisher owned by John Wiley & Sons. It was founded in 1921 as Verlag Chemie (meaning "Chemistry Press": VCH stands for ''Verlag Chemie'') by two German learned societies. Later, it was merged into the German Chemical Soci ...
, Weinheim.
Crystal violet
Crystal violet or gentian violet, also known as methyl violet 10B or hexamethyl pararosaniline chloride, is a triarylmethane dye used as a histological stain and in Gram's method of classifying bacteria. Crystal violet has antibacterial, antif ...
.
Image:NewFuchsineStructure.png, New fuchsine dye.
File:Pararosaniline.png, Pararosaniline
Pararosaniline, Basic Red 9, or C.I. 42500 is an organic compound with the formula H2NC6H4)3Cl. It is a magenta solid with a variety of uses as a dye. It is one of the four components of basic fuchsine. (The others are rosaniline, new fuchsine ...
See also
*Triphenylmethane
Triphenylmethane, or triphenyl methane, is the hydrocarbon with the formula (C6H5)3CH. This colorless solid is soluble in nonpolar organic solvents and not in water. Triphenylmethane is the basic skeleton of many synthetic dyes called triarylmeth ...
*Triphenylmethanol
Triphenylmethanol (also known as triphenylcarbinol, TrOH) is an organic compound. It is a white crystalline solid that is insoluble in water and petroleum ether, but well soluble in ethanol, diethyl ether, and benzene. In strongly acidic solutions ...
References
PubChem ID 2723954 - Triphenylcarbenium hexafluorophosphate
. Entry in NCBI's PubChem database, accessed on 2019-07-25.